|
|

Cloud Computing
It is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. You typically pay only for cloud services you use, helping you lower your operating costs, run your infrastructure more efficiently, and scale as your business needs change.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Predictive Cost Considerations
- Scalability
- Performance
- Security
- Speed
- Productivity
- Reliability
Types of Cloud Computing
-
Public Cloud
-
Private Cloud
-
Hybrid Cloud
Public Cloud
Public clouds are the most common type of cloud computing deployment. The cloud resources (like servers and storage) are owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider and delivered over the internet. With a public cloud, all hardware, software, and other supporting infrastructure are owned and managed by the cloud provider. Microsoft Azure is an example of a public cloud.In a public cloud, you share the same hardware, storage, and network devices with other organizations or cloud “tenants,” and you access services and manage your account using a web browser. Public cloud deployments are frequently used to provide web-based email, online office applications, storage, and testing and development environments.
The three largest public cloud providers include Microsoft Azure, Amazon web services(AWS) and google cloud platform. Customers can take advantage of services such as computing power, storage space, infrastructure, applications and much more from the various providers.
Advantages of public clouds:
Lower costs - no need to purchase hardware or software, and you pay only for the service you use.No maintenance - your service provider provides the maintenance.
Near-unlimited scalability- on-demand resources are available to meet your business needs.
High reliability - a vast network of servers ensures against failure.
Private Cloud
A private cloud consists of cloud computing resources used exclusively by one business or organization. The private cloud can be physically located at your organization’s on-site datacenter, or it can be hosted by a third-party service provider. But in a private cloud, the services and infrastructure are always maintained on a private network and the hardware and software are dedicated solely to your organization.In this way, a private cloud can make it easier for an organization to customize its resources to meet specific IT requirements. Private clouds are often used by government agencies, financial institutions, any other mid- to large-size organizations with business-critical operations seeking enhanced control over their environment.
Advantages of a private cloud:
More flexibility - your organization can customize its cloud environment to meet specific business needs.More control - resources are not shared with others, so higher levels of control and privacy are possible.
More scalability - private clouds often offer more scalability compared to on-premises infrastructure.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is a type of cloud computing that combines on-premises infrastructure- or a private cloud- with a public cloud. Hybrid clouds allow data and apps to move between the two environments.Many organizations choose a hybrid cloud approach due to business imperatives such as meeting regulatory and data sovereignty requirements, taking full advantage of on-premises technology investment, or addressing low latency issues.
The hybrid cloud is evolving to include edge workloads as well. Edge computing brings the computing power of the cloud to IoT devices-closer to where the data resides. By moving workloads to the edge, devices spend less time communicating with the cloud, reducing latency, and they are even able to operate reliably in extended offline periods.
Cloud Computing Services
-
IaaS
-
PaaS
-
SaaS
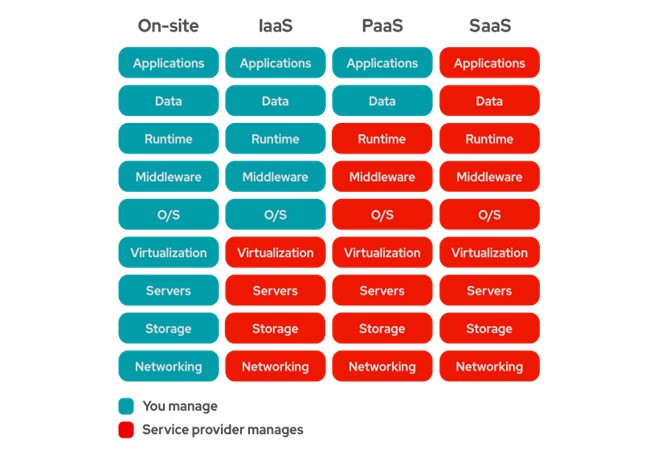
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
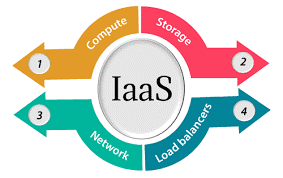
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is a type of cloud computing service that offers essential compute, storage, and networking resources on demand, on a pay-as-you-go basis. IaaS is one of the four types of cloud services, along with software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and serverless.
Migrating your organization's infrastructure to an IaaS solution helps you reduce maintenance of on-premises data centers, save money on hardware costs, and gain real-time business insights. IaaS solutions give you the flexibility to scale your IT resources up and down with demand. They also help you quickly provision new applications and increase the reliability of your underlying infrastructure.
IaaS lets you bypass the cost and complexity of buying and managing physical servers and datacenter infrastructure. Each resource is offered as a separate service component, and you only pay for a particular resource for as long as you need it. A cloud computing service provider like Azure manages the infrastructure, while you purchase, install, configure, and manage your own software—including operating systems, middleware, and applications.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
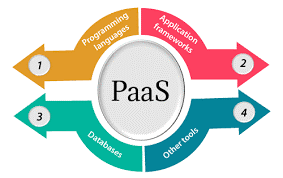
Platform as a service (PaaS) is a complete development and deployment environment in the cloud, with resources that enable you to deliver everything from simple cloud-based apps to sophisticated, cloud-enabled enterprise applications. You purchase the resources you need from a cloud service provider on a pay-as-you-go basis and access them over a secure Internet connection.
Like IaaS, PaaS includes infrastructure—servers, storage, and networking—but also middleware, development tools, business intelligence (BI) services, database management systems, and more. PaaS is designed to support the complete web application lifecycle: building, testing, deploying, managing, and updating.
PaaS allows you to avoid the expense and complexity of buying and managing software licenses, the underlying application infrastructure and middleware, container orchestrators such as Kubernetes, or the development tools and other resources. You manage the applications and services you develop, and the cloud service provider typically manages everything else.
Software as a Service(SaaS)
Software as a service (SaaS) allows users to connect to and use cloud-based apps over the Internet. Common examples are email, calendaring, and office tools (such as Microsoft Office 365).
SaaS provides a complete software solution that you purchase on a pay-as-you-go basis from a cloud service provider. You rent the use of an app for your organization, and your users connect to it over the Internet, usually with a web browser. All of the underlying infrastructure, middleware, app software, and app data are located in the service provider’s data center. The service provider manages the hardware and software, and with the appropriate service agreement, will ensure the availability and the security of the app and your data as well. SaaS allows your organization to get quickly up and running with an app at minimal upfront cost.